We all do our best to ensure a happy and healthy workforce. That’s why, in a perfect world, you would never have to create an incident report.
But since incidents do happen, it’s never a bad idea to be prepared for any situation–especially the unexpected.
Small business owners, human resources teams and workplace emergency first responders: this is the article for you!
In this step-by-step guide, I’ll share our top tips on creating incident reports that will help you carry out effective investigations and make sure similar (or more serious) incidents don’t happen again. I’ll also include our top incident report templates to get the job done.
Table of Contents:
- What is an incident report?
- Incident report sample
- What to include in a work incident report?
- How to write an incident report?
- Incident report examples, templates and design tips
- 5 types of incidents reports
- Incident report legal considerations
All of the templates in this post can be customized using our free online incident report maker tool.
What is an incident report?
An incident report is a crucial document that records workplace injuries, near misses, and accidents to ensure accountability and facilitate improvements in workplace safety. It should be completed at the time an incident occurs no matter how minor an injury is.
Here’s one example:
Any illness or injury that impacts an employee’s ability to work must be noted. While specific legal requirements vary by jurisdiction, incident reports typically need to include details such as the date, time, location of the incident, a description of what happened, and any witnesses present.
If you’re unsure, you can take a look at your government’s website for more details. In certain cases, there are exceptions that can exempt small businesses from complying with such legislation.
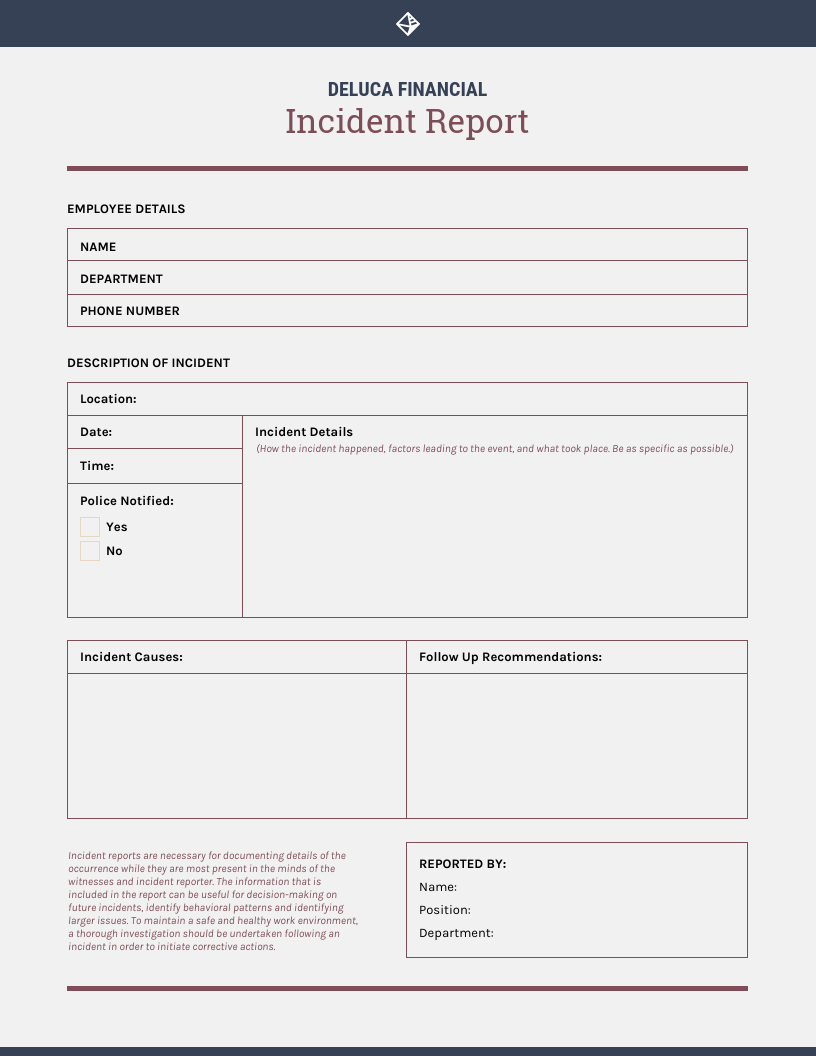
Incident report sample
Here’s an example of a completed incident report:
Name:
John Smith
Department:
Maintenance
Phone Number:
(555) 123-4567
Incident Location:
Warehouse B, Loading Dock
Date:
July 1, 2024
Time:
3:15 PM
Incident Description:
At approximately 3:15 PM on July 8, 2024, a pallet of boxes fell from a forklift at the loading dock of Warehouse B. The forklift operator, Jane Smith, was moving the pallet when it tipped over, causing several boxes to fall and spill their contents onto the floor. One of the boxes struck the leg of another employee, Michael Brown, causing a minor injury.
Incident Causes:
The incident was primarily caused by the pallet being improperly secured on the forklift, compounded by the forklift operator potentially making a sharp turn, which led to the pallet tipping over. Additionally, the cluttered area around the loading dock restricted movement and contributed to the incident.
Follow-up Recommendations:
To prevent similar incidents in the future, it is recommended to conduct thorough inspections of all forklifts and ensure that pallets are properly secured before moving. Additional training should be provided for forklift operators on safe handling and maneuvering of loads. Furthermore, maintaining a clutter-free environment around the loading dock is essential to ensure safe operations. Regular safety audits should be implemented to identify and address potential hazards promptly. Finally, ensuring that all employees are aware of and follow safety protocols is crucial to prevent future incidents.
Employee signature: John Smith
Additional witnesses signatures: May Lee, Tamara Johnson
What to include in a work incident report?
A well-structured incident report typically includes the following five key elements:
- Date, time and location: Provide specific details about when and where the incident occurred. This information helps establish a timeline and context for understanding the event.
- Description of the incident: Clearly describe what happened, including relevant details such as the sequence of events, the people involved and any contributing factors. Use objective language and avoid assumptions or opinions. For instance, instead of saying ‘The employee was careless,’ state ‘The employee slipped on a wet floor.’
- Witness information: Include names and contact information for any witnesses to the incident, ensuring their privacy is respected in the reporting process. Their accounts can provide valuable perspectives and corroborate details.
- Action taken: Outline any immediate actions taken to address the incident, such as first aid, evacuation procedures or contacting emergency services. Documenting these responses is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of the initial response.
- Recommendations for prevention: Offer suggestions on how similar incidents can be prevented in the future. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to improving safety and mitigating risks.
Related: How to Write a Professional Progress Report
How to write an incident report?
To write any incident case reports, follow the basic format described below.
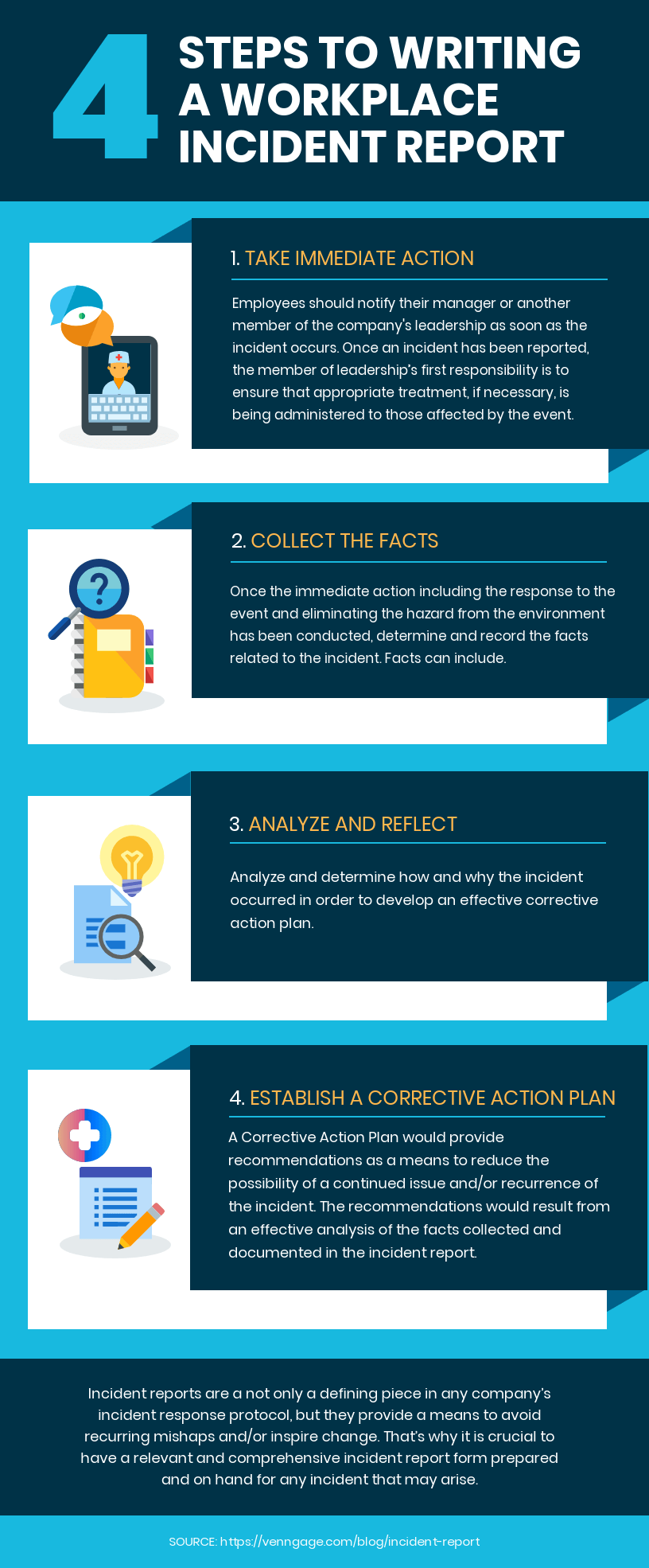
Step 1. Take immediate action
Employees of your organization should notify their manager or another member of the company’s leadership committee as soon as an incident occurs, regardless of the nature of the event (whether it be an accident, illness, injury or near miss).
Define clear communication channels to encourage employees to report incidents.
Once an incident has been reported, the leadership’s first responsibility is to ensure that appropriate treatment, if necessary, is being administered to those affected by the event.
On this note: If the hazard still exists, the manager that the event has been reported to must eliminate the hazard promptly. Each company should have a defined procedure for accomplishing this based on the nature of their work.
For example, if a spill causes a fall, attend to the victim, clean the spill, and mark the area as hazardous with a sign.
Step 2. Collect the facts
Once the immediate action including the response to the event and eliminating the hazard from the environment has been conducted, it’s time to determine and record the facts related to the incident details.
9 facts related to the incident include:
1. The basics
Identify the specific location, time and date of the incident. This information is fundamental to the investigation and the most obvious information to collect.
2. The affected
Collect details of those involved and/or affected by the incident. This would entail recording the name(s) of the individual(s) involved, their job title(s), the department(s) they operate in the manager(s) of those affected.
3. The witnesses
Speak to any witnesses of the event to collect their perspectives of the event. Record their statements as detailed and accurate as possible in the form.
To ensure accuracy, it’s best practice to review your notes with the witness to ensure they agree with how the event is portrayed in the report. It’s also important to include the name(s) of any witnesses in the report in case any additional questioning is required.
4. The context
Document the events leading up to the incident. Ask questions such as:
- What was the employee doing?
- Who asked them to complete the task?
- How was the employee feeling prior to the incident? …etc.
It is important to identify which factors were an outcome of the incident and which factors were present prior to the incident and could be a potential contributing factor to the incident occurring.
5. The actions
In the report, you must specify the actions of those involved at the time of the incident. What did the employee do that led to the incident?
For example, if an employee injured their back when lifting a box at work, it is important to determine how that employee lifted the box to decide if that contributed to the injury. If yes, then inquire if this employee was trained properly for this task and by who or what source.
6. The environment
Identify environmental conditions contributing to the incident, such as inadequate lighting, malfunctioning equipment, or obstructed visibility.
7. The injuries
Record detailed descriptions of specific injuries and evaluate the severity of such in the report. This description should include part(s) of the body injured, nature and extent of injuries.
8. The treatment
It is also important to document in the incident case report the type of treatment administered for the acknowledged injuries. This information is important to document in order to understand how the employee recovers when reviewing the specifics of the event.
9. The damages
Record an account of any damage to equipment, materials, etc that was affected by the incident. This will be helpful to refer back during the analysis of the event in order to consider both a corrective action plan and to determine what items will need to be repaired or replaced.
Step 3. Analyze and reflect
Collecting and recording facts is essential for understanding how and why the incident occurred.
Analyzing and determining how and why the incident occurred is essential in order to develop an effective corrective action plan.
Potential causes for accidents or injuries that occurred in the workplace could include:
- Primary causes (for example, an unsalted ice patch on a set of stairs that caused a slip and fall).
- Secondary causes (for example, an employee not wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as a hard helmet or eyewear).
- Other contributing causes (for example: a burned-out light bulb in the area causing poor visibility).
Step 4. Establish a corrective action plan
A corrective action plan provides recommendations to reduce the risk of recurring incidents. The recommendations would result from an effective analysis of the facts collected and documented in the incident report.
Elements of an effective corrective action plan could include:
- Providing occupational health & safety training for employees
- Performing preventative routine maintenance processes that ensure equipment is in proper working condition
- A review of job practices and procedures with a recommendation for changes to reduce the risk of incidents
- Conducting a job hazard analysis to determine if other potential hazards are associated with the task and/or environment and then training employees on these hazards based on the findings of the assessment
- Engineering, equipment or PPE changes/upgrades to ensure the task or the process of completing said task poses less risk
Incident report examples, templates and design tips
Here are some examples of types of incident reports to help you get started. I’ve also included some report design tips to help you present your information effectively. If you want to dig a bit deeper into the topic, here’s a comprehensive guide to general report design to get started.
Incorporating branding into your report design
As with any document you create for your business, it’s good practice to incorporate your branding into your incident reports. (Psst–Venngage’s Brand Kit feature makes it easy to add your branding in just a click!)
Include your brand colors in your design. You can do this by using them in the report header, footer, sidebar and in any visuals.
You could use your brand colors in the background of your incident report:
You may also want to include your logo, like in this incident report template:
Organize information into sections using boxes
To make your information as readable as possible, organize it into sections. One of the easiest ways to do this is by using boxes.
For example, take a look at how these types of incident report templates use boxes to section off the information:
This type of incident report example also uses rectangles to denote section headers:
Color code sections for better readability
Colors aren’t just great for making your reports, presentations and charts more interesting to look at. You can also use color to organize sections of your report and to draw attention to key information.
For more tips on using color in your designs, read our guide on how to pick colors to communicate effectively.
Add a visual header to incident report
As part of your company branding, you may want to add a visual header to your reports. For example, this incident case report template uses a neutral photo with a color filter to create a professional header:
You can do this in Venngage by overlaying a photo on a color background and adjusting the opacity of the photo:

You can use the same effect for sidebars as well:
Create mock form to train new employees
If you’re transitioning in staff or something happens when the individual who owns incident reports is away, it’s very important that there is a process documented. That will ensure that if someone is put on the spot, they can fill in the incident report properly.
It can also be helpful to add brief descriptions of the information in the type of incident report to include in each field. Take a look at how this incident report example offers some brief text to guide the person filling it out:
Use icons to visualize key concepts
Icons are small, compact visuals that can be used to reinforce the information in your reports. You can also use them to draw attention to specific fields and important pieces of information.
For example, this incident case report template uses icons to indicate the purpose of each field:
Establishing a systematic method for investigating incidents is important for accurate reporting and effective analysis.
Additionally, It’s also equally important to prepare a report that allows you to document every relevant aspect of the incident. This is the essential first step in the incident reporting process.
After you’ve created your incident report form, you can:
- Begin your investigation with fact-finding
- And end your investigation with determining recommendations for preventing both an increase in the severity of the incident and the possibility of a recurrence.
Related: 20 Professional Report Cover Page Examples & Templates
5 types of incident reports
Incident reports vary depending on the nature of the incident and the environment in which it occurred. Here are some common types of incident reports:
Workplace accident reports
These reports document injuries or accidents that happen in the workplace and often used for OSHA compliance.
Security incident reports
These reports are used to document breaches, thefts, or security-related incidents, including unauthorized access or loss of property.
Customer incident reports
These reports are filed when a customer experiences an accident or issue on company property, such as a slip and fall, food-related illness, or a product malfunction.
Safety incident reports
These reports record incidents related to workplace safety, such as equipment malfunctions, hazardous spills, or unsafe working conditions.
HR incident reports
HR incident reports are formal records that document events or issues involving employees in the workplace. These reports are crucial for maintaining a safe, respectful, and compliant work environment.
Incident report legal considerations
Incident reporting, particularly in workplace or healthcare settings, requires careful consideration in order to avoid legal consequences. Here are a few of them:
Regulatory compliance
Many industries are subject to specific regulations that mandate incident reporting, such as OSHA in the US for workplace safety or HIPAA for patient privacy in healthcare.
In industrial settings, understanding common forklift hazards helps contextualize equipment-related incidents and improve the specificity of reports. Failure to comply with these reporting requirements can result in fines, sanctions, or legal action.
Employee rights and protections
Employees involved in or reporting an incident have certain legal rights, including protection against retaliation. Laws such as whistleblower protections safeguard employees who report misconduct or safety violations. Retaliatory actions can lead to legal action against the organization.
Retention and accessibility of records
Organizations must retain incident reports for a designated period, as these records may be required in future legal cases or audits. Following record retention laws ensures that reports are accessible when needed and that they are disposed of properly when no longer required.
Related: 12+ Sales Report Examples to Boost Your Business & How to Create Them
FAQs about incident reports
What is the purpose of incident reporting?
An incident report is used to describe an event that requires an investigation that needs to be documented.
What are the different types of incident reports?
- Accident Reports: Documents any accident that results in injury, damage, or harm, usually in a workplace or public setting.
- Workplace Incident Report: Records any event in the workplace that leads to injury, damage, or a near miss.
- Edit Form: It is a type of document or interface used to modify or update existing reports or records
What are the 4 types of incidents?
Commonly, incidents can be categorized into four main types:
- Accidents: Involving unintended harm, damage or injury.
- Near Misses: Situations where an accident could have occurred but was narrowly avoided.
- Unsafe Conditions: Reports about hazardous or unsafe environments that need attention.
- Unsafe Acts: Documenting incidents involving violations of safety procedures or rules.
Incident reports generally cover a variety of situations and the specific types may vary based on context and industry. It’s important to note that these categories can overlap and the classification may differ depending on the reporting system or industry standards.
What distinguishes an incident report from other documents (e.g., police report)?
An incident report is used to document workplace injuries or accidents. It is primarily used for internal uses, especially stakeholder reporting. Incident reports help assess the injury or accident and find its root cause. However, other documents like police reports document criminal activities and are used in legal proceedings.
When should an incident be reported?
An incident should be reported as soon as possible after it’s taken place. This helps investigate the cause of the incident and prevent similar accidents in the future.
Create incident reports easily with Venngage
Preparing for the unexpected is challenging, but preventative measures are key to maintaining a safe, healthy workplace.
Incident reports are essential to incident response plans and help prevent recurring issues or inspire change.
That’s why it is crucial to have a relevant and comprehensive incident report form prepared and on hand for any incident details that may arise. Ensure compliance with legislation and adopt the four key components discussed above to handle incidents effectively.
The effect of responding to workplace incidents in a timely and detail-oriented manner will not only ensure a safe workplace but also:
- Reassure employees that their employer is prepared to act in any situation .
- Keep all stakeholders informed of the incident.
- Establish a record of incidents for future reference.
- Protect the company and employees from legal disputes.
However, writing incident reports from scratch requires a lot of time and effort. You can simplify the process with Venngage’s professional incident report templates. The best part is you can customize the the template to match your brand guidelines.
More HR guides and templates: