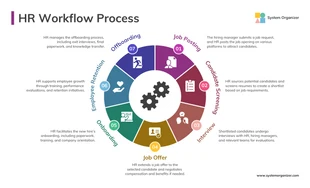
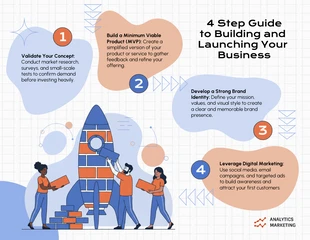
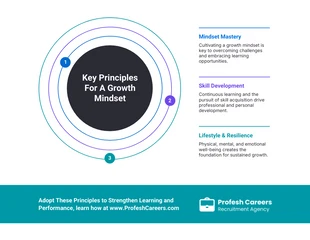
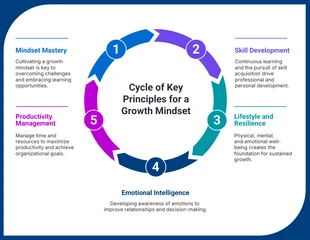
Narrative Text Infographic Template
Create brand stories to show consumers how your brand fits their everyday lives by personalizing this narrative infographic.
100% customizable templates
Millions of photos, icons, charts and graphics
AI-powered editing features
Effortlessly share, download, embed and publish
Easily generate QR codes for your designs
- Design stylemodern
- Colorslight
- SizeCustom (816 x 2580 px)
- File typePNG, PDF, PowerPoint
- Planfree
A narrative connects events by idea, plot, or concept to make a good story. Narratives have been in existence since the beginning of storytelling. They are used in many forms of writing, such as essays, biographies, and novels. The word "narrative" can refer to a specific genre of literature—such as the love story—or an entire mode of human expression, as in the narrating of epic tales and personal experiences. In its broadest sense, the narration is simply an instance of written or spoken communication. In commonplace usage, however, "narration" most often refers to storytelling: the recitation of events in chronological order such that they constitute a coherent whole. What makes a particular instance of narration interesting or significant is its ability to connect individual elements in a pattern that readers or listeners can follow. The act or process of narration—of constructing a story from individual events—is an art and a practice. It involves shaping events around an overarching set of aims or effects (consciously or unconsciously). For example, in a comedic narrative, the overriding aim is to surprise/shock or otherwise lead